Vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin, is a vital nutrient for various bodily functions and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It comes in two main forms: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2 (menaquinone). While both forms are important, they differ in their sources, functions, and benefits. In this blog, we will explore the benefits and uses of vitamin K, delve into the differences between vitamin K and K2, and address potential side effects.
What Does Vitamin K Do?
Vitamin K is primarily known for its role in blood clotting. It aids in the production of several clotting factors that are essential for the coagulation process, preventing excessive bleeding in case of injury. Additionally, vitamin K also plays a vital role in maintaining bone health and regulating calcium metabolism, making it crucial for proper bone development and preventing osteoporosis.
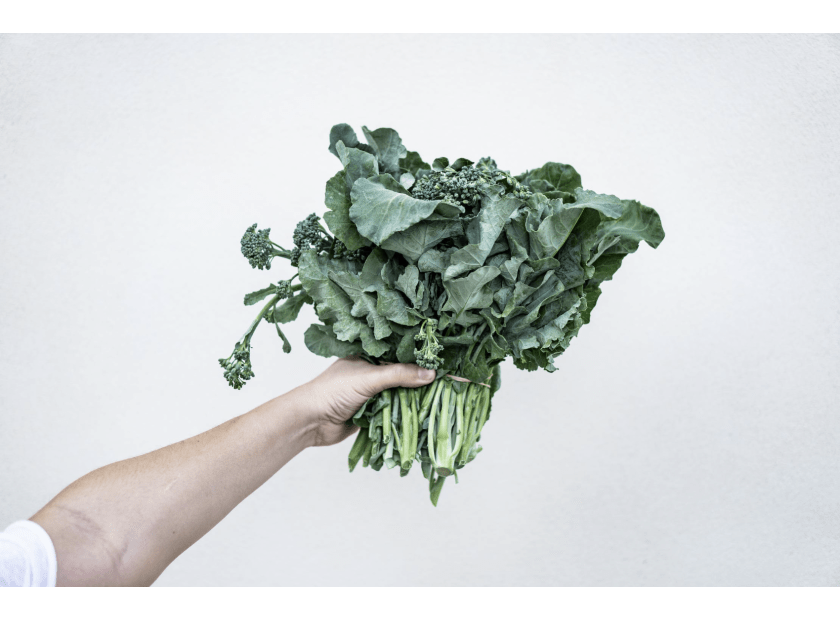
Vitamin K1, which is predominantly found in leafy green vegetables like kale, spinach, and broccoli, is essential for blood clotting. It helps activate clotting proteins in the liver, which ensures that blood clots properly and prevents excessive bleeding.
On the other hand, vitamin K2 is produced by bacteria in the intestines and can also be obtained from certain fermented foods like natto, sauerkraut, and cheese. Vitamin K2 has unique benefits, including its ability to activate proteins that help regulate calcium distribution in the body. By directing calcium away from arteries and soft tissues, vitamin K2 plays a vital role in preventing cardiovascular diseases, such as arterial calcification.
What Is Vitamin K Good For?
Blood Clotting
Vitamin K is essential for the production of clotting factors that help control bleeding. Adequate intake of vitamin K can reduce the risk of excessive bleeding and haemorrhages.
Bone Health
Vitamin K, particularly vitamin K2, is crucial for bone health. It helps activate osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to the bone matrix, promoting bone mineralisation and preventing the loss of bone density.
Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin K2's ability to regulate calcium metabolism helps prevent calcium deposition in arteries and blood vessels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis.
Cognitive Function
Some studies suggest that vitamin K may play a role in brain health and cognitive function, although more research is needed to fully understand this connection.
Vitamin K2 Side Effects
While vitamin K is generally considered safe when consumed through food sources or as recommended dietary supplements, excessive intake can lead to certain side effects. It is important to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult a healthcare professional before taking vitamin K supplements.
Excessive intake of vitamin K supplements can cause blood clotting problems, particularly in individuals taking anticoagulant medications like warfarin. These medications work by inhibiting the action of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, and an excess of vitamin K can interfere with their effectiveness.
Vitamin K for Newborns
Newborn infants are often given a vitamin K injection shortly after birth. This is done to prevent a rare but potentially serious condition called vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB), which can cause bleeding in the brain or other organs. The injection helps ensure that newborns have adequate levels of vitamin K to support proper blood clotting.
Functions of Vitamin K in the Body
As well as its role in blood clotting, bone health, and cardiovascular function, vitamin K has other important functions in the body:
Wound Healing
Vitamin K plays a role in the healing process by supporting the production of proteins that aid in tissue repair.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Some studies suggest that vitamin K has anti-inflammatory effects, which may be beneficial for conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Cancer Prevention
Research is ongoing to explore the potential role of vitamin K in preventing certain types of cancer, such as liver and prostate cancer. However, more studies are needed to establish a definitive link.
Difference Between Vitamin K and K2
The main difference between vitamin K and K2 lies in their sources and functions. Vitamin K1 is primarily found in plant-based foods, while vitamin K2 is synthesised by bacteria in the intestines or obtained from fermented foods. Vitamin K1 is important for blood clotting, while vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in calcium metabolism and bone health.
We stock The Good Guru K2 capsules for vegans and Solgar Vitamin K1 tablets, shop our full range of supplements and vitamins for a healthy and well-balanced lifestyle.
Health Benefits of Vitamin K
The health benefits of vitamin K are numerous and diverse. From ensuring proper blood clotting to supporting bone health and cardiovascular function, vitamin K is an essential nutrient for overall well-being. Including vitamin K-rich foods in your diet, such as leafy greens, broccoli, and fermented foods, can help ensure you meet your daily requirements.
Conclusion
Vitamin K is a vital nutrient with a range of benefits and uses. It is essential for blood clotting, bone health, cardiovascular function, and more. While vitamin K1 is primarily involved in blood clotting, vitamin K2 is essential for calcium metabolism and bone health. By incorporating vitamin K-rich foods into your diet or considering appropriate supplementation, you can support your overall health and well-being.
As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalised advice regarding your specific dietary needs and any potential interactions with medications. Shop Total Body Cares' range of Vitamin K supplements today.